Caen Basket Calvados Players on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Caen (, ; nrf, Kaem) is a
INSEE, retrieved 20 June 2022. making Caen the second largest urban area in
 During the
During the

Twisto - Les Mobilités de Caen la mer
Normandie. Derniers ajustements pour les nouveaux horaires des trains en 2020
while Railcoop will soon open new lines such as Lille-Amiens-Rouen-Caen-Rennes-Nantes and Paris-Caen-Brest making Caen railway station his hub of the North-Wes
Caen railway Station is the second busiest of Normandy after Rouen's one
Air France va proposer 5 destinations depuis Caen-Carpiquet en 2022


 Caen was the birthplace or origin of:
Caen was the birthplace or origin of:
 *
*
 *
*
 *
*
 From 1947 to 2006, Caen was a stage of the Tour de France a total of 15 times. Further, Caen was one of the hosts of the EuroBasket 1983. The city has a football team, Stade Malherbe Caen, SM Caen. The Drakkars de Caen play ice hockey in the FFHG Division 1. In 2014, Caen was the location of the 2014 FEI World Equestrian Games.
From 1947 to 2006, Caen was a stage of the Tour de France a total of 15 times. Further, Caen was one of the hosts of the EuroBasket 1983. The city has a football team, Stade Malherbe Caen, SM Caen. The Drakkars de Caen play ice hockey in the FFHG Division 1. In 2014, Caen was the location of the 2014 FEI World Equestrian Games.
File:Blason ville fr Caen ancien.svg,
File:Blason Caen 1809.svg,
File:Blason ville fr Caen (Calvados) Empire (Orn ext).svg,
File:Blason ville fr Caen (Calvados) (Orn ext).svg,
File:Escoville Angle.jpg, Hôtel d'Escoville, 16th century, Caen
File:Chateau_Caen.jpg, South Wall of the Castle, a huge fortress in the centre of the city
File:Caen Hôtel de Ville.JPG, Town Hall of Caen
File:Caen gare bv.jpg, Caen railway station
File:Tramway de Caen Station.jpg, Caen's former 'tramway' was in fact a modern guided-bus system.
File:Normandie Calvados Caen6 tango7174.jpg, Saint-Étienne-le-Vieux Church
File:Caen-1.JPG, Interior of Saint-Pierre Church
File:Caen-2.JPG, The fortress of Caen
File:Caen-3.JPG, The Abbey of St. Étienne
File:Église Saint Pierre seen from in front of the Château.jpg, Église Saint Pierre seen from in front of the Château
Publications du CRAHM
Caen City Council
*
Encyclopædia Britannica Caen
Mémorial pour la Paix museum
Caen town guide
{{Authority control Caen, Communes of Calvados (department) Prefectures in France Port cities and towns on the French Atlantic coast Cities in France
commune
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to:
Administrative-territorial entities
* Commune (administrative division), a municipality or township
** Communes of ...
in northwestern France. It is the prefecture
A prefecture (from the Latin ''Praefectura'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain international ...
of the department
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
of Calvados
Calvados (, , ) is a brandy from Normandy in France, made from apples or pears, or from apples with pears.
History In France
Apple orchards and brewers are mentioned as far back as the 8th century by Charlemagne. The first known record of Norm ...
. The city proper has 105,512 inhabitants (), while its functional urban area
The larger urban zone (LUZ), or functional urban area (FUA), is a measure of the population and expanse of metropolitan and surrounding areas which may or may not be exclusively urban. It consists of a city and its commuting zone outside it.
Th ...
has 470,000,Comparateur de territoireINSEE, retrieved 20 June 2022. making Caen the second largest urban area in
Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
and the 19th largest in France. It is also the third largest commune in all of Normandy after Le Havre
Le Havre (, ; nrf, Lé Hâvre ) is a port city in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region of northern France. It is situated on the right bank of the estuary of the river Seine on the Channel southwest of the Pays de Caux, very cl ...
and Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of ...
.
It is located inland from the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
, north-west of Paris, and connected to the south of England by the Caen (Ouistreham
Ouistreham () is a commune in the Calvados department in Normandy region in northwestern France.
Ouistreham is a small port with fishing boats, leisure craft and a ferry harbour. It serves as the port of the city of Caen. The town borders the mo ...
) to Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
ferry route. Caen is located in the centre of its northern region, and it is a centre of political, economic and cultural power. Located a few miles from the coast, the landing beaches, the bustling resorts of Deauville
Deauville () is a commune in the Calvados department, Normandy, northwestern France. Major attractions include its harbour, race course, marinas, conference centre, villas, Grand Casino, and sumptuous hotels. The first Deauville Asian Film Fes ...
and Cabourg
Cabourg (; nrf, Cabouorg) is a commune in the Calvados department, region of Normandy, France. Cabourg is on the coast of the English Channel, at the mouth of the river Dives. The back country is a plain, favourable to the culture of cereal. Th ...
, as well as Norman Switzerland
Norman Switzerland (french: Suisse Normande) is a part of Normandy, France, in the border region of the departments Calvados and Orne. Its name comes from its rugged and verdant relief resembling the Swiss Alps, with gorges carved by the river Orn ...
and Pays d'Auge
The Pays d'Auge (, literally ''Land of Auge'') is an area in Normandy, straddling the ''départements'' of Calvados and Orne (plus a small part of the territory of Eure). The chief town is Lisieux.
Geography
Generally it consists of the basin of ...
, Caen is often considered the archetype of Normandy.
Caen is known for its historical buildings built during the reign of William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first House of Normandy, Norman List of English monarchs#House of Norman ...
, who was buried there, and for the Battle for Caen
The Battle for Caen (June to August 1944) is the name given to fighting between the British Second Army and the German in the Second World War for control of the city of Caen and its vicinity during the larger Battle of Normandy. The battles ...
, heavy fighting that took place in and around Caen during the Battle of Normandy
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) with the Norma ...
in 1944, destroying much of the city. The city has now preserved the memory by erecting a memorial and a museum dedicated to peace, the Mémorial de Caen
The Mémorial de Caen is a museum and war memorial in Caen, Normandy, France commemorating World War II and the Battle for Caen. More generally, the museum is dedicated to the history of the twentieth century, mainly focused on the fragility o ...
.
History
Early history
Caen was known in Roman times as 'Catumagos', from the Gaulish roots ''magos'' meaning 'field' and ''catu'' meaning 'combat'. It remained a minor settlement throughout the Roman period and began to see major development commence in the 10th century, under the patronage of the Dukes of Normandy. Around 1060,William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first House of Normandy, Norman List of English monarchs#House of Norman ...
began construction of the Château de Caen The Château de Caen is a castle in the Norman city of Caen in the Calvados ''département'' (Normandy). It has been officially classed as a ''Monument historique'' since 1997.
History
The castle was built c. 1060 by William the Conqueror (Will ...
, which became the centre of the ducal court. Duchess Matilda of Flanders
Matilda of Flanders (french: link=no, Mathilde; nl, Machteld) ( 1031 – 2 November 1083) was Queen of England and Duchess of Normandy by marriage to William the Conqueror, and regent of Normandy during his absences from the duchy. She was t ...
also founded the Benedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, foun ...
Abbey of Sainte-Trinité, Caen
The Abbey of Sainte-Trinité (french: Abbaye de la Sainte-Trinité), better known as the Abbaye aux Dames, is a former nunnery in Caen, Normandy, now home to the Regional Council of Normandy. The complex includes the Church of Sainte-Trinité ...
around the same time, eventually being buried in the abbey. Caen succeeded Bayeux
Bayeux () is a Communes of France, commune in the Calvados (department), Calvados Departments of France, department in Normandy (administrative region), Normandy in northwestern France.
Bayeux is the home of the Bayeux Tapestry, which depicts ...
as the capital of Lower Normandy
Lower Normandy (french: Basse-Normandie, ; nrf, Basse-Normaundie) is a former administrative region of France. On 1 January 2016, Lower and Upper Normandy merged becoming one region called Normandy.
Geography
The region included three departme ...
, complementing the second ducal capital of Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of ...
.
Caen fell to Philip II of France
Philip II (21 August 1165 – 14 July 1223), byname Philip Augustus (french: Philippe Auguste), was King of France from 1180 to 1223. His predecessors had been known as kings of the Franks, but from 1190 onward, Philip became the first French ...
on 21 May 1204, and was incorporated along with the remainder of Normandy into the Kingdom of France.
Hundred Years' War
In 1346, KingEdward III of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring ro ...
led his army against the city, hoping to loot it. It was expected that a siege of perhaps several weeks would be required, but the army took the city in less than a day, on 26 July 1346, storming and sacking it, killing 3,000 of its citizens, and burning much of the merchants' quarter on the Île Ste-Jean. Only the castle of Caen held out, despite attempts to besiege it. A few days later, the English left, marching to the east and on to their victory at the Battle of Crécy
The Battle of Crécy took place on 26 August 1346 in northern France between a French army commanded by King PhilipVI and an English army led by King EdwardIII. The French attacked the English while they were traversing northern France du ...
. It was later captured following a siege by Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (c. 1173–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (121 ...
in 1417 and treated harshly for being the first town to put up any resistance to his invasion. In 1450 towards the end of the war, French forces recaptured Caen.
Second World War
 During the
During the Battle of Normandy
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) with the Norma ...
in the Second World War, Caen was taken back from German forces in early July, a month after the Normandy landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as ...
, particularly those by British I Corps on 6 June 1944. British and Canadian troops had intended to capture the town on D-Day
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as D ...
. However they were held up north of the city until 9 July, when an intense bombing campaign during Operation Charnwood
Operation Charnwood was an Anglo-Canadian offensive that took place from 8 to 9 July 1944, during the Battle for Caen, part of the larger Operation Overlord (code-name for the Battle of Normandy) in the Second World War. The operation was in ...
destroyed 70% of the city and killed 2,000 French civilians. The Allies seized the western quarters, a month later than Field Marshal Montgomery
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein, (; 17 November 1887 – 24 March 1976), nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and ...
's original plan. During the battle, many of the town's inhabitants sought refuge in the ''Abbaye aux Hommes'' ("Men's Abbey"), built by William the Conqueror some 800 years before. The spire of the Church of Saint-Pierre, Caen
The Church of Saint-Pierre (french: Église Saint-Pierre) is a Roman Catholic church located on the Place Saint-Pierre in the centre of Caen in Normandy, northern France. It is dedicated to Saint Peter.
Known as ''Saint-Pierre of Darnetal'', ''S ...
and the university were destroyed by the British and Canadian bombing.
Postwar
Postwar work included the reconstruction of complete districts of the city and the university campus. It took 14 years (1948–1962) and led to the current urbanization of Caen. Having lost many of its historic quarters and its university campus in the war, Caen does not have the atmosphere of a traditional Norman town such asHonfleur
Honfleur () is a commune in the Calvados department in northwestern France. It is located on the southern bank of the estuary of the Seine across from le Havre and very close to the exit of the Pont de Normandie. The people that inhabit Honf ...
, Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of ...
, Cabourg
Cabourg (; nrf, Cabouorg) is a commune in the Calvados department, region of Normandy, France. Cabourg is on the coast of the English Channel, at the mouth of the river Dives. The back country is a plain, favourable to the culture of cereal. Th ...
, Deauville
Deauville () is a commune in the Calvados department, Normandy, northwestern France. Major attractions include its harbour, race course, marinas, conference centre, villas, Grand Casino, and sumptuous hotels. The first Deauville Asian Film Fes ...
or Bayeux
Bayeux () is a Communes of France, commune in the Calvados (department), Calvados Departments of France, department in Normandy (administrative region), Normandy in northwestern France.
Bayeux is the home of the Bayeux Tapestry, which depicts ...
.
The Canadian Army Film and Photo Unit filmed the D-Day offensive and Orne breakout several weeks later. It returned several months later to document the city's recovery efforts. The resulting film, ''You Can't Kill a City'', is preserved in the National Archives of Canada
Library and Archives Canada (LAC; french: Bibliothèque et Archives Canada) is the federal institution, tasked with acquiring, preserving, and providing accessibility to the documentary heritage of Canada. The national archive and library is t ...
.
Etymology
The very first mentions of the name of Caen are found in different acts of the dukes ofNormandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
: ''Cadon'' 1021/1025, ''Cadumus'' 1025, ''Cathim'' 1026/1027. Year 1070 of the Parker manuscript of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alf ...
'' refers to Caen as ''Kadum'', and year 1086 of the Laud manuscript gives the name as ''Caþum''. Despite a lack of sources as to the origin of the settlements, the name Caen would seem to be of Gaulish
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic languages, Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium ...
origin, from the words ''catu-'', referring to military activities and ''magos'', field, hence meaning "manoeuvre field" or "battlefield". In Layamon
Layamon or Laghamon (, ; ) – spelled Laȝamon or Laȝamonn in his time, occasionally written Lawman – was an English poet of the late 12th/early 13th century and author of the ''Brut'', a notable work that was the first to present the legend ...
's ''Brut'', the poet asserts that King Arthur
King Arthur ( cy, Brenin Arthur, kw, Arthur Gernow, br, Roue Arzhur) is a legendary king of Britain, and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In the earliest traditions, Arthur appears as a ...
named the city in memory of Sir Kay
In Arthurian legend, Sir Kay ( cy, Cai, Middle Welsh ''Kei'' or ''Cei''; la, Caius; French: ''Keu''; Old French: ''Kès'' or ''Kex'') is King Arthur's foster brother and later seneschal, as well as one of the first Knights of the Round Table. ...
.
Geography
Caen is in an area of high humidity. The riverOrne
Orne (; nrf, Ôrne or ) is a département in the northwest of France, named after the river Orne. It had a population of 279,942 in 2019.Channel
Channel, channels, channeling, etc., may refer to:
Geography
* Channel (geography), in physical geography, a landform consisting of the outline (banks) of the path of a narrow body of water.
Australia
* Channel Country, region of outback Austral ...
. A canal (Canal de Caen à la Mer
Canal de Caen à la Mer ( en, Canal from Caen to the sea, also called the "Caen Canal") is a short canal in the department (préfecture) of Calvados, France, connecting the Port of Caen, in the city of Caen, downstream to the town of Ouistreham ...
) parallel to the Orne was built during the reign of Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew ...
to link the city to the sea at all times. The canal reaches the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
at Ouistreham
Ouistreham () is a commune in the Calvados department in Normandy region in northwestern France.
Ouistreham is a small port with fishing boats, leisure craft and a ferry harbour. It serves as the port of the city of Caen. The town borders the mo ...
. A lock keeps the tide out of the canal and lets large ships navigate up the canal to Caen's freshwater harbours.
Population
The population data in the table and graph below refer to the commune of Caen proper, in its geography at the given years. The commune of Caen absorbed the former commune ofVenoix Venoix is a western quarter of Caen, in Calvados, France. It was an independent commune
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to:
Administrative-territorial ...
in 1952.
Main sights
Castle
The castle, ''Château de Caen The Château de Caen is a castle in the Norman city of Caen in the Calvados ''département'' (Normandy). It has been officially classed as a ''Monument historique'' since 1997.
History
The castle was built c. 1060 by William the Conqueror (Will ...
'', built circa 1060 by William the Conqueror, who successfully conquered England in 1066, is one of the largest medieval fortresses of Western Europe. It remained an essential feature of Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
strategy and policy. At Christmas 1182, a royal court
A royal court, often called simply a court when the royal context is clear, is an extended royal household in a monarchy, including all those who regularly attend on a monarch, or another central figure. Hence, the word "court" may also be appl ...
celebration for Christmas in the aula
The Canadian Aviation Regulations define two types of ultralight aircraft: basic ultra-light aeroplane (BULA), and advanced ultra-light aeroplane (AULA).
Definition
Regulation of ultra-light aircraft in Canada is covered by the Canadian A ...
of Caen Castle brought together Henry II and his sons, Richard the Lionheart
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199) was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Aquitaine and Gascony, Lord of Cyprus, and Count of Poitiers, Anjou, Maine, and Nantes, and was overl ...
and John Lackland
John (24 December 1166 – 19 October 1216) was King of England from 1199 until his death in 1216. He lost the Duchy of Normandy and most of his other French lands to King Philip II of France, resulting in the collapse of the Angevin Empi ...
, receiving more than a thousand knights. Caen Castle, along with all of Normandy, was handed over to the French Crown in 1204. The castle saw several engagements during the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
(1346, 1417, 1450) and was in use as a barracks as late as the Second World War. Bullet holes are visible on the walls of the castle where members of the French Resistance
The French Resistance (french: La Résistance) was a collection of organisations that fought the German occupation of France during World War II, Nazi occupation of France and the Collaborationism, collaborationist Vichy France, Vichy régim ...
were shot during the Second World War. Today, the castle serves as a museum that houses the ''Musée des Beaux-Arts de Caen'' (Museum of Fine Arts
In European academic traditions, fine art is developed primarily for aesthetics or creative expression, distinguishing it from decorative art or applied art, which also has to serve some practical function, such as pottery or most metalwork ...
of Caen) and ''Musée de Normandie'' (Museum of Normandy) along with many periodical exhibitions about arts and history. (See )
Abbeys
In repentance for marrying his cousinMathilda of Flanders
Matilda of Flanders (french: link=no, Mathilde; nl, Machteld) ( 1031 – 2 November 1083) was Queen of England and Duchess of Normandy by marriage to William the Conqueror, and regent of Normandy during his absences from the duchy. She was t ...
, William ordered two abbey
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christian monks and nuns.
The conce ...
s to be built on the Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
's encouragement:
* Eglise St.-Etienne, formerly the ''Abbaye aux Hommes'' (Men's Abbey). It was completed in 1063 and is dedicated to St Stephen
Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ''Stéphanos'', meaning "wreath, crown" and by extension "reward, honor, renown, fame", often given as a title rather than as a name; c. 5 – c. 34 AD) is traditionally venerated as the protomartyr or first ...
. The current ''Hôtel de Ville'' (town hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
) of Caen is built onto the South Transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform churches, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave in a cruciform ("cross-shaped") building withi ...
of the building.
* ''Eglise de la Ste.-Trinité'', formerly the ''Abbaye aux Dames'' (Women's Abbey). It was completed in 1060 and is dedicated to the Holy Trinity
The Christian doctrine of the Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the central dogma concerning the nature of God in most Christian churches, which defines one God existing in three coequal, coeternal, consubstantial divine persons: God the F ...
. The current seat of the regional council (''conseil régional
A regional council (french: conseil régional) is the elected assembly of a region of France.
History
Regional councils were created by law on 5 July 1972. Originally they were simply consultative bodies consisting of the region's parliamentary ...
'') of Basse-Normandie is nearby.
Others
* Jardin botanique de Caen, a historicbotanical garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens, an ...
* Church of Saint-Pierre
* Church of Saint-Étienne-le-Vieux
* Church of Saint-Jean de Caen
* ''Mémorial pour la Paix'' ("Memorial for Peace") built in 1988, a museum charting the events leading up to and after D-Day
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as D ...
. It is an emotional presentation inviting meditation on the thought of Elie Wiesel
Elie Wiesel (, born Eliezer Wiesel ''Eliezer Vizel''; September 30, 1928 – July 2, 2016) was a Romanian-born American writer, professor, political activist, Nobel Peace Prize, Nobel laureate, and Holocaust survivor. He authored Elie Wiesel b ...
: "Peace is not a gift from God to man, but a gift from man to himself". The Memorial for Peace also includes an exhibit of Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Chemi ...
winners and another one on Conflict Resolution
Conflict resolution is conceptualized as the methods and processes involved in facilitating the peaceful ending of conflict and retribution. Committed group members attempt to resolve group conflicts by actively communicating information abou ...
in different cultures.
* Parc Festyland
Parc Festyland is a relatively small theme park situated within the Caen ringroad (A13/A84) in Lower Normandy, France. Sometimes referred to as being in Carpiquet in Greater Caen, the theme park receives approximately 110,000 visitors a year.
...
, an amusement park
An amusement park is a park that features various attractions, such as rides and games, as well as other events for entertainment purposes. A theme park is a type of amusement park that bases its structures and attractions around a central ...
to the west of Caen in the nearby town of Carpiquet. The park receives 110,000 visitors every year.
* Mondeville 2
Mondeville 2 is a shopping mall, shopping centre in Caen, France, and the largest of the Lower Normandy region. It is situated in the suburb of Caen in the town of Mondeville, Calvados, Mondeville.
The shopping centre was built by the Promodès ...
is a regional shopping centre in adjoining Mondeville.
* Medieval wooden houses
* Colline aux Oiseaux, a floral parc located on the former dump of the city of Caen
Administration
Mayors of Caen
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well a ...
have included:
* 1945–1959: Yves Guillou
Yves Guillou (16 December 1880 – 27 February 1963) was a French politician. He was the first mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there i ...
, Rally of the French People
The Rally of the French People (french: Rassemblement du Peuple Français, RPF) was a French political party, led by Charles de Gaulle.
Foundation
The RPF was founded by Charles de Gaulle in Strasbourg on 14 April 1947, one year after his resign ...
* 1959–1970: Jean-Marie Louvel
Jean-Marie Louvel (1 July 1900 – 13 June 1970) was a French engineer and politician.
1900 births
1970 deaths
People from Orne
Politicians from Normandy
Popular Republican Movement politicians
French Ministers of Commerce and I ...
, MRP and Centre Démocrate
* 1970–2001: Jean-Marie Girault, Republican Party and UDF
* 2001–2008: Brigitte Le Brethon
Brigitte Le Brethon (born 8 March 1951) is a French politician, and a member of The Republicans. She was born in Campeaux, Calvados, France.
She was the mayor of Caen from 2001 to 2008. She was Caen's first woman mayor and was defeated in Ma ...
, RPR and UMP
* 2008–2014: Philippe Duron
Philippe Duron (born 19 June 1947) is a French politician. He was the mayor of Caen between 2008 and 2014 and deputy for Calvados's 1st constituency.
Philippe Duron received a degree in history in 1975 and was a teacher until 1997. His polit ...
, PS
* 2014–present: Joël Bruneau
Joël Bruneau (born 7 September 1963) is a French politician, mayor of Caen since 2014. He was reelected in 2020.
Distinctions
* Chevalier of the Légion d'honneur.
See also
* List of mayors of Caen
This is a list of mayors of Caen s ...
, The Republicans
Joël Bruneau was re-elected mayor in the 2020 municipal elections.
In 1952, the small commune of Venoix Venoix is a western quarter of Caen, in Calvados, France. It was an independent commune
A commune is an alternative term for an intentional community. Commune or comună or comune or other derivations may also refer to:
Administrative-territorial ...
became part of Caen.
In 1990, the agglomeration of Caen was organized into a district, transformed in 2002 into a ''Communauté d'agglomération
An agglomeration community (french: communauté d'agglomération) is a government structure in France, created by the Chevènement Law of 1999. It is one of four forms of intercommunality, less integrated than a métropole or a communauté urb ...
'' (''Grand Caen'' (Greater Caen), renamed Caen la Mer
Caen (, ; nrf, Kaem) is a commune in northwestern France. It is the prefecture of the department of Calvados. The city proper has 105,512 inhabitants (), while its functional urban area has 470,000,Villons-les-Buissons
Villons-les-Buissons () is a commune in the Calvados department in the Normandy region in northwestern France.
Population
See also
*Communes of the Calvados department
The following is a list of the 528 communes of the Calvados depar ...
, Lion-sur-Mer
Lion-sur-Mer (, literally ''Lion on Sea'') is a commune in the Calvados department in the Normandy region in northwestern France.
Geography
Lion-sur-Mer is located on the edge of the English Channel, more precisely on the '' Côte de Nacre'' ...
, Hermanville-sur-Mer
Hermanville-sur-Mer () is a Communes of France, commune in the Calvados (department), Calvados Departments of France, department in the Normandy (administrative region), Normandy Regions of France, region in northwestern France.
Population
Sig ...
, which joined the Communauté d'agglomération in 2004. The population of the "communauté d'agglomération" is around 220,000 inhabitants.
In the former administrative organisation, Caen was a part of 9 cantons
A canton is a type of administrative division of a country. In general, cantons are relatively small in terms of area and population when compared with other administrative divisions such as counties, departments, or provinces. Internationally, t ...
, of which it was the chief town. These cantons contained a total of 13 towns. Caen gave its name to a 10th canton, of which it was not part. Since the 2015 canton reorganization, Caen is part of the cantons of Caen-1, 2, 3, 4 and 5.
Transport
Public transport
Twisto Twisto is the urban transport network of Caen Including about sixty bus lines and 3 tramway linesTwisto - Les Mobilités de Caen la mer
Rail
Caen also had several main andbranch railway
A branch line is a phrase used in railway terminology to denote a secondary railway line which branches off a more important through route, usually a main line. A very short branch line may be called a spur line.
Industrial spur
An industr ...
lines linking Caen railway station to all parts of Normandy with lines to Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, Vire
Vire () is a town and a former commune in the Calvados department in the Normandy region in northwestern France. On 1 January 2016, it was merged into the new commune of Vire Normandie.
Geography
The town is located on the river Vire. Much of it ...
, Flers, Cabourg
Cabourg (; nrf, Cabouorg) is a commune in the Calvados department, region of Normandy, France. Cabourg is on the coast of the English Channel, at the mouth of the river Dives. The back country is a plain, favourable to the culture of cereal. Th ...
, Houlgate
Houlgate () is a small tourist resort in northwestern France along the English Channel with a beach and a casino. It is a commune in the Calvados department in the Normandy region.
History
Pre-19th century
Houlgate developed as a hamlet in t ...
, Deauville
Deauville () is a commune in the Calvados department, Normandy, northwestern France. Major attractions include its harbour, race course, marinas, conference centre, villas, Grand Casino, and sumptuous hotels. The first Deauville Asian Film Fes ...
, Saint-Lô
Saint-Lô (, ; br, Sant Lo) is a commune in northwest France, the capital of the Manche department in the region of Normandy.Bayeux
Bayeux () is a Communes of France, commune in the Calvados (department), Calvados Departments of France, department in Normandy (administrative region), Normandy in northwestern France.
Bayeux is the home of the Bayeux Tapestry, which depicts ...
and Cherbourg
Cherbourg (; , , ), nrf, Chèrbourg, ) is a former commune and subprefecture located at the northern end of the Cotentin peninsula in the northwestern French department of Manche. It was merged into the commune of Cherbourg-Octeville on 28 Feb ...
.
Now the SNCF is taking care of Paris-Caen-Cherbourg, Caen-Rouen, Caen-Le Mans
Le Mans (, ) is a city in northwestern France on the Sarthe River where it meets the Huisne. Traditionally the capital of the province of Maine, it is now the capital of the Sarthe department and the seat of the Roman Catholic diocese of Le Man ...
-Tours, Caen-Rennes
Rennes (; br, Roazhon ; Gallo: ''Resnn''; ) is a city in the east of Brittany in northwestern France at the confluence of the Ille and the Vilaine. Rennes is the prefecture of the region of Brittany, as well as the Ille-et-Vilaine department ...
and some others small lineNormandie. Derniers ajustements pour les nouveaux horaires des trains en 2020
while Railcoop will soon open new lines such as Lille-Amiens-Rouen-Caen-Rennes-Nantes and Paris-Caen-Brest making Caen railway station his hub of the North-Wes
Caen railway Station is the second busiest of Normandy after Rouen's one
Air transport
Caen - Carpiquet Airport
Caen (, ; nrf, Kaem) is a commune in northwestern France. It is the prefecture of the department of Calvados. The city proper has 105,512 inhabitants (), while its functional urban area has 470,000,HOP!
Air France Hop, formerly branded HOP!, is a French regional airline operating flights on behalf of its parent company Air France. The airline was founded on 21 December 2012http://www.verif.com/societe/HOP!-790151716/ after the merger of Airlin ...
, Volotea and the French national airline
A flag carrier is a transport company, such as an airline or shipping company, that, being locally registered in a given sovereign state, enjoys preferential rights or privileges accorded by the government for international operations.
Hist ...
Air France
Air France (; formally ''Société Air France, S.A.''), stylised as AIRFRANCE, is the flag carrier of France headquartered in Tremblay-en-France. It is a subsidiary of the Air France–KLM Group and a founding member of the SkyTeam global air ...
operates flights to the French cities of Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of t ...
, Nice, Toulouse, Montpellier, Marseille, Biarritz, Ajaccio, Figari, Bastia and CalviAir France va proposer 5 destinations depuis Caen-Carpiquet en 2022
Water transport
Caen is served by the large port ofOuistreham
Ouistreham () is a commune in the Calvados department in Normandy region in northwestern France.
Ouistreham is a small port with fishing boats, leisure craft and a ferry harbour. It serves as the port of the city of Caen. The town borders the mo ...
, lying at the mouth of the Caen Canal
Caen (, ; nrf, Kaem) is a commune in northwestern France. It is the prefecture of the department of Calvados. The city proper has 105,512 inhabitants (), while its functional urban area has 470,000,English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
. A cruise/ferry service operates between Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
, England, and Caen/Ouistreham running both standard roll-on-roll-off car ferries and supercat fast ferries, with the latter making crossing from March to November. The ferry terminal is from Caen with a daytime shuttle bus service for foot passengers. There's also a cyclist road from Caen to Ouistreham.
Road transport
Caen is connected to the rest of France bymotorways
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms i ...
to Paris ( A13), Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known ...
and Southern France ( A84) and to Le Mans
Le Mans (, ) is a city in northwestern France on the Sarthe River where it meets the Huisne. Traditionally the capital of the province of Maine, it is now the capital of the Sarthe department and the seat of the Roman Catholic diocese of Le Man ...
and central France ( A88– A28). The A13 and A88 are toll road
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road (almost always a controlled-access highway in the present day) for which a fee (or ''toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically implemented ...
s while the A84 is a toll-free motorway. The city is encircled by the N814 ring-road (Boulevard Périphérique) that was completed in the late 1990s. The N13 connects Caen to Cherbourg
Cherbourg (; , , ), nrf, Chèrbourg, ) is a former commune and subprefecture located at the northern end of the Cotentin peninsula in the northwestern French department of Manche. It was merged into the commune of Cherbourg-Octeville on 28 Feb ...
and to Paris. A section of the former N13 (Caen-Paris) is now D613 (in Calvados) following road renumbering. The Boulevard Périphérique includes an impressive viaduct
A viaduct is a specific type of bridge that consists of a series of arches, piers or columns supporting a long elevated railway or road. Typically a viaduct connects two points of roughly equal elevation, allowing direct overpass across a wide v ...
called the Viaduc de Calix that goes over the canal and River Orne
The Orne () is a river in Normandy, within northwestern France. It is long. It discharges into the English Channel at the port of Ouistreham. Its source is in Aunou-sur-Orne, east of Sées. Its main tributaries are the Odon and the Rouvre.
The ...
. The canal links the city to the sea to permit cargo ship
A cargo ship or freighter is a merchant ship that carries cargo, goods, and materials from one port to another. Thousands of cargo carriers ply the world's seas and oceans each year, handling the bulk of international trade. Cargo ships are usu ...
s and ferries to dock in the port of Caen
The Port of Caen (French: ''Port de Caen)'' is the harbour and port authority of the Norman city of Caen, France.
The port of Caen is composed of a series of basins on the Canal de Caen à la Mer, linking Caen to Ouistreham, 15 km (9.3&nbs ...
. Ferries which have docked include the ''Quiberon
Quiberon (; , ) is a commune in the French department of Morbihan, administrative region of Brittany, western France.
It is situated on the southern part of the Quiberon peninsula, the northern part being the commune of Saint-Pierre-Quiberon. It ...
'' and the '' Duc de Normandie''.
Education
* TheUniversity of Caen
The University of Caen Normandy (French: ''Université de Caen Normandie''), also known as Unicaen, is a public university in Caen, France.
History
The institution was founded in 1432 by John of Lancaster, 1st Duke of Bedford, the first rector ...
has around 34,000 students in five different campuses and Caen is ranked 18th biggest student city of France. The University has a good reputation as it is ranked 16th in France.
* The University is divided into 11 colleges, called ''UFR'' (''Unité fondamentale de Recherche''), six institutes, one Engineering School, two IUP and five local campuses. The University is one of the oldest in France, having been founded by Henry VI, King of England
Henry VI (6 December 1421 – 21 May 1471) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1422 to 1461 and again from 1470 to 1471, and disputed King of France from 1422 to 1453. The only child of Henry V, he succeeded to the English thron ...
in 1432.
* Caen also has a school of fine arts L'ésam Caen/Cherbourg and ''grandes écoles Grandes may refer to:
* Agustín Muñoz Grandes, Spanish general and politician
*Banksia ser. Grandes, a series of plant species native to Australia
* Grandes y San Martín, a municipality located in the province of Ávila, Castile and León, Spain ...
'' such as the École nationale supérieure d'ingénieurs de Caen and École supérieure d'ingénieurs des travaux de la construction de Caen
École supérieure d'ingénieurs des travaux de la construction de Caen (ESITC Caen) a French engineering College created in 1993.
The school trains engineers for the construction industry and with the support of local authorities.
Located in Ca ...
.
* A campus of the business school École de management de Normandie
The École de Management de Normandie (also known as EM Normandie Business School) is a business school created in 1871. Incorporated as a Higher Education & Research non-profit association (under the 1901 Act) and operating under private law, i ...
is also located in the city.

Economy
Theagricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
and food-processing Agrial
Agrial is a French agricultural cooperative and food-processor with operations in dairy, beef, poultry, vegetables and fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flower ...
cooperative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-control ...
has its head office on Caen. Agrial group processes vegetable
Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the flowers, fruits, stems, ...
s, cider apple
Cider apples are a group of apple cultivars grown for their use in the production of cider (referred to as "hard cider" in the United States). Cider apples are distinguished from "cookers" and "eaters", or dessert apples, by their bitterness or ...
s, milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. Immune factors and immune ...
, poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for their eggs, their meat or their feathers. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes (which includes chickens, quails, a ...
and meat
Meat is animal flesh that is eaten as food. Humans have hunted, farmed, and scavenged animals for meat since prehistoric times. The establishment of settlements in the Neolithic Revolution allowed the domestication of animals such as chic ...
with the help of its 12,000 employees and all its partners.
Music and theatre
The Théâtre de Caen (1963) is the home of theBaroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
musical ensemble
A musical ensemble, also known as a music group or musical group, is a group of people who perform instrumental and/or vocal music, with the ensemble typically known by a distinct name. Some music ensembles consist solely of instrumentalists, ...
Les Arts Florissants. The organization was founded by conductor William Christie in 1979 and derives its name from the 1685 opera by Marc-Antoine Charpentier
Marc-Antoine Charpentier (; 1643 – 24 February 1704) was a French Baroque composer during the reign of Louis XIV. One of his most famous works is the main theme from the prelude of his ''Te Deum'', ''Marche en rondeau''. This theme is still us ...
.
Notable people

 Caen was the birthplace or origin of:
Caen was the birthplace or origin of:Public service
*Robert, 1st Earl of Gloucester
Robert FitzRoy, 1st Earl of Gloucester (c. 1090 – 31 October 1147 David Crouch, 'Robert, first earl of Gloucester (b. c. 1090, d. 1147)’, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, 2004; online edn, May 200Retrieved ...
(ca.1090–1147), illegitimate son of Henry I of England
Henry I (c. 1068 – 1 December 1135), also known as Henry Beauclerc, was King of England from 1100 to his death in 1135. He was the fourth son of William the Conqueror and was educated in Latin and the liberal arts. On William's death in ...
.
* Robert Constantin (ca.1530 – 1605), physician, bibliographer, lexicographer and humanist.
* Samuel Bochart
Samuel Bochart (30 May 1599 – 16 May 1667) was a French Protestant biblical scholar, a student of Thomas Erpenius and the teacher of Pierre Daniel Huet. His two-volume '' Geographia Sacra seu Phaleg et Canaan'' (Caen 1646) exerted a profound in ...
(1599–1667 in Caen), Protestant biblical scholar, taught Pierre Daniel Huet
image:Portret van Pierre-Daniel Huet Petrus Daniel Huetius (titel op object), RP-P-BI-7523.jpg, P. D. Huetius
Pierre Daniel Huet (; la, Huetius; 8 February 1630 – 26 January 1721) was a French churchman and scholar, Editing, editor of the Delph ...
.
* St. John Eudes
John Eudes, CIM (french: link=no, Jean Eudes; 14 November 1601 – 19 August 1680) was a French people, French Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic priest and the founder of both the Order of Our Lady of Charity in 1641 and Congregation of Jes ...
(1601–1680), Catholic priest, forerunner of the devotion
Devotion or Devotions may refer to:
Religion
* Faith, confidence or trust in a person, thing, or concept
* Anglican devotions, private prayers and practices used by Anglican Christians
* Buddhist devotion, commitment to religious observance
* Cat ...
to the Sacred Heart
The Most Sacred Heart of Jesus ( la, Cor Jesu Sacratissimum) is one of the most widely practised and well-known Catholic devotions, wherein the heart of Jesus is viewed as a symbol of "God's boundless and passionate love for mankind". This devo ...
.
* Tanneguy Le Fèvre (1615–1672), classical scholar.
* Pierre Daniel Huet
image:Portret van Pierre-Daniel Huet Petrus Daniel Huetius (titel op object), RP-P-BI-7523.jpg, P. D. Huetius
Pierre Daniel Huet (; la, Huetius; 8 February 1630 – 26 January 1721) was a French churchman and scholar, Editing, editor of the Delph ...
(1630–1721), churchman and scholar.
* Gervais de La Rue (1751–1835), historian, re. Norman language
Norman or Norman French (, french: Normand, Guernésiais: , Jèrriais: ) is a Romance language which can be classified as one of the Oïl languages along with French, Picard and Walloon. The name "Norman French" is sometimes used to descri ...
and Anglo-Norman literature Anglo-Norman may refer to:
*Anglo-Normans, the medieval ruling class in England following the Norman conquest of 1066
*Anglo-Norman language
**Anglo-Norman literature
* Anglo-Norman England, or Norman England, the period in English history from 106 ...
* Louis Gustave le Doulcet, comte de Pontécoulant
Louis Gustave le Doulcet, comte de Pontécoulant (17 November 1764 – 3 April 1853) was a French politician. He was the father of Louis Adolphe le Doulcet and Philippe Gustave le Doulcet.
Biography
Early life and National Convention
Born ...
(1764–1853), politician.
* Charlotte Corday
Marie-Anne Charlotte de Corday d'Armont (27 July 1768 – 17 July 1793), known as Charlotte Corday (), was a figure of the French Revolution. In 1793, she was executed by guillotine for the assassination of Jacobin leader Jean-Paul Marat, who w ...
(1768–1793), guillotined
A guillotine is an apparatus designed for efficiently carrying out executions by beheading. The device consists of a tall, upright frame with a weighted and angled blade suspended at the top. The condemned person is secured with stocks at the ...
for the assassination of Jean-Paul Marat
Jean-Paul Marat (; born Mara; 24 May 1743 – 13 July 1793) was a French political theorist, physician, and scientist. A journalist and politician during the French Revolution, he was a vigorous defender of the ''sans-culottes'', a radical ...
* Charles Mathieu Isidore Decaen
Charles Mathieu Isidore Decaen (, 13 April 1769 – 9 September 1832) was a French general who served during the French Revolutionary Wars, as Governor General of Pondicherry and the Isle de France (now Mauritius) and as commander of the Army ...
(1769–1832), a French general.
* Eugène Poubelle
Eugène-René Poubelle (15 April 1831 – 15 July 1907) was a French lawyer and diplomat who introduced waste containers to Paris and made their use compulsory. This introduction was so innovative at the time that Poubelle's surname became synony ...
(1831–1907), lawyer and diplomat, introduced waste container
A waste container, also known as a dustbin, garbage can, and trash can is a type of container that is usually made out of metal or plastic. The words "rubbish", "basket" and "bin" are more common in British English usage; "trash" and "can" a ...
s to Paris
* Charles-Hippolyte Pouthas (1886–1974), historian of political and religious history
* Marie-Pierre Kœnig
Marie Joseph Pierre François Kœnig or Koenig (10 October 1898 – 2 September 1970) was a French general during World War II during which he commanded a Free French Brigade at the Battle of Bir Hakeim in North Africa in 1942. He started a pol ...
(1898–1970), Maréchal de France
Marshal of France (french: Maréchal de France, plural ') is a French military distinction, rather than a military rank, that is awarded to generals for exceptional achievements. The title has been awarded since 1185, though briefly abolished (1 ...
, commanded the Free French
Free France (french: France Libre) was a political entity that claimed to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third Republic. Led by French general , Free France was established as a government-in-exile ...
at the Battle of Bir Hakeim
The Battle of Bir Hakeim () took place at Bir Hakeim, an oasis in the Libyan desert south and west of Tobruk, during the Battle of Gazala (26 May – 21 June 1942). The 1st Free French Brigade under Marie-Pierre Kœnig defended the position from ...
* Claude Hettier de Boislambert (1906-1986), Resistance leader, governor, politician, diplomat
* Ovida Delect (1926–1996), poet, Communist, politician, member of the French resistance
The French Resistance (french: La Résistance) was a collection of organisations that fought the German occupation of France during World War II, Nazi occupation of France and the Collaborationism, collaborationist Vichy France, Vichy régim ...
in WWII and a trans woman
A trans woman or a transgender woman is a woman who was assigned male at birth. Trans women have a female gender identity, may experience gender dysphoria, and may transition; this process commonly includes hormone replacement therapy and so ...
.
* Sonia de La Provôté
Sonia de La Provôté (born 25 December 1968) is a French politician, member of the French Senate. She was elected in 2017 and again in 2020. She represents the department of Calvados
Calvados (, , ) is a brandy from Normandy in France, ma ...
(born 1968), member of the French Senate
The Senate (french: Sénat, ) is the upper house of the French Parliament, with the lower house being the National Assembly (France), National Assembly, the two houses constituting the legislature of France. The French Senate is made up of 34 ...
* Fabrice Le Vigoureux (born 1969), member of the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repre ...
The Arts
 *
* Jean Bertaut
Jean Bertaut (1552 – 8 June 1611), French poet, was born at Caen.
Life
He figures with Philippe Desportes in the disdainful couplet of Boileau on Ronsard:
"''Ce poëte orgueilleux, trébuché de si haut,''
''Rendit plus retenus Desport ...
(1552–1611), poet of light verse to celebrate the incidents of court life.
* François de Malherbe
François de Malherbe (, 1555 – 16 October 1628) was a French poet, critic, and translator.
Life
He was born in Le Locheur (near Caen, Normandie), to a family of standing, although the family's pedigree did not satisfy the heralds in terms of ...
(1555 at Le Locheur – 1628), poet, critic and translator.
* François le Métel de Boisrobert
François le Métel de Boisrobert (1 August 1592 – 30 March 1662) was a French poet, playwright, and courtier.
Life
He was born in Caen. He trained as a lawyer, later practising for a time in Rouen. He traveled to Paris in 1622 and establis ...
(1592–1662), poet, playwright and courtier.
* Jean François Sarrazin
Jean François Sarrazin (c. 1611 – 5 December 1654), or Sarasin, was a French writer.
Biography
Sarrazin was born at Hermanville, near Caen, the son of Roger Sarasin, treasurer-general at Caen.
He was educated at Caen, and later settled in ...
(ca.1611 at Hermanville – 1654), a French writer.
* René Auguste Constantin de Renneville
René Auguste Constantin de Renneville (October 9, 1650 – March 13, 1723), was a French writer.
He was born in Caen. Because of his Protestant principles, Renneville left France for the Netherlands in 1699. On his return three years later h ...
(1650–1723), writer.
* Jean-Baptiste Belin (1653–1715), painter who specialized in flowers.
* François Henri Turpin (1709–1799), man of literature.
* J. Hector St. John de Crèvecœur (1735–1813), French-American writer
* Jean-Jacques Boisard (1744–1833), writer who specialized in fable
Fable is a literary genre: a succinct fictional story, in prose or verse, that features animals, legendary creatures, plants, inanimate objects, or forces of nature that are anthropomorphized, and that illustrates or leads to a particular mo ...
s
* Jean-François Boisard (1762–1820), painter and poet.
* Daniel Auber
Daniel-François-Esprit Auber (; 29 January 178212 May 1871) was a French composer and director of the Paris Conservatoire.
Born into an artistic family, Auber was at first an amateur composer before he took up writing operas professionally when ...
(1782–1871), composer and director of the Paris Conservatoire
The Conservatoire de Paris (), also known as the Paris Conservatory, is a college of music and dance founded in 1795. Officially known as the Conservatoire National Supérieur de Musique et de Danse de Paris (CNSMDP), it is situated in the avenue ...
.
* Étienne Mélingue (1807–1875), actor, sculptor and painter.
* Jules Danbé
Jules Danbé (16 November 1840 – 30 October 1905) was a French violinist, composer and conductor, mainly of opera.
Biography
Danbé was born in Caen, Calvados. Trained as a violinist, he was a pupil of Narcisse Girard and Marie Gabriel Augu ...
(1840–1905), a violinist, composer and conductor, mainly of opera.
* Gabriel Dupont
Gabriel Édouard Xavier Dupont (1 March 1878 – 1 August 1914) was a French composer, known for his operas and chamber music.
Biography
Dupont was born in Caen. Following after his father who was a teacher at the Malherbe secondary school and t ...
(1878–1914), composer of operas and chamber music.
* Roger Grenier
Roger Grenier (19 September 1919 – 8 November 2017) was a French writer, journalist and radio animator. He was Regent of the Collège de ’Pataphysique.
Biography
As a youth, Grenier lived in Pau, where Andrélie opened a shop selling gla ...
(1919–2017), writer, journalist and radio animator.
* Alain Duhamel (born 1940), journalist and political commentator.
* Jean-Loup Rivière (1948–2018), playwright and drama critic.
* Laure Adler
Laure Adler ( née Laure Clauzet; born 11 March 1950, in Caen) is a French journalist, writer, publisher and radio/TV producer.
Works
Biographies
* 1986: ''L'Amour à l'arsenic : histoire de Marie Lafarge'', Denoël.
* 1998: ''Marguerite ...
(born 1950), journalist, writer, publisher and radio/TV producer.
* Christophe Desjardins
Christophe Desjardins (24 April 1962 – 13 February 2020) was a French violist and specialist in contemporary music.
Biography
Born in Caen, Christophe Desjardins entered the Conservatoire de Paris in 1982, at the age of 20, in Serge Collot' ...
(born 1962), a viola player and specialist in contemporary music.
* Olivier Baroux
Olivier Baroux (born 5 January 1964) is a French actor, comedian, writer and director who has acted both on stage and on screen. He first became known in forming with Kad Merad
Kad Merad (born Kaddour Merad, ar, قدور ميراد, link=no; ...
(born 1964), actor, comedian, writer and director
* Gilles Peterson
Gilles Jérôme Moehrle MBE (; born 28 September 1964), better known as Gilles Peterson (), is a French broadcaster, DJ, and record label owner. He founded the influential labels Acid Jazz and Talkin' Loud, and started his current label Brown ...
(born 1964), DJ, record collector, record label owner; lives in London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
* Laurent Lefrançois
file:MSL-Lefrancois.jpg,
Laurent Lefrançois (born in 1974 in Caen) is a French composer.
Life
Winner of the Claude Arrieu Prize of the Sacem in 2016 and public prize at the international competition for young composers in Boulogne in 2006 ( ...
(born 1974), French contemporary composer
* Orelsan
Aurélien Cotentin (; born 1 August 1982), better known by his stage name Orelsan, sometimes stylized as OrelSan (), is a French rapper, songwriter, record producer, actor and film director. He has released four studio albums: his debut ''Perdu d ...
(born 1982), rapper, songwriter, record producer, actor and film director
Science & Business
 *
* Pierre Varignon
Pierre Varignon (1654 – 23 December 1722) was a French mathematician. He was educated at the Jesuit College and the University of Caen, where he received his M.A. in 1682. He took Holy Orders the following year.
Varignon gained his first ex ...
(1654–1722), mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems.
Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change.
History
On ...
, he invented the U-tube manometer
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressur ...
* Estienne Roger
Estienne Roger (1664 or 1665 in Caen, France – 7 July 1722 in Amsterdam) was a francophone printer, bookseller and publisher of sheet music working in the Netherlands.
Life
Roger was born a French Huguenot. The revocation of Edict of Nantes ...
(ca.1664 – 1722), printer, bookseller and publisher of sheet music
* Paul Jacques Malouin
Paul Jacques Malouin (27 June 1701 – 3 January 1778) was a French physician and chemist.
Career
Born in Caen, Malouin graduated in medicine in 1730 against the wishes of his father (a legal official from Caen) who had sent him to Paris to study ...
(1701–1778), physician and chemist.
* Guillaume-François Rouelle (1703 at Mathieu – 1770), chemist and apothecary.
* Louis Lépecq de La Clôture (1736-1804), surgeon and epidemiologist
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidenc ...
.
* Pierre-Simon Girard
Pierre-Simon Girard (4 November 1765 – 30 November 1836) was a French mathematician and engineer, who worked on fluid mechanics.
Girard was born in Caen. A prodigy who invented a water turbine at the age of ten, he worked as an engineer at th ...
(1765–1836), mathematician and engineer, worked on fluid mechanics.
* Hippolyte-Victor Collet-Descotils (1773–1815), chemist; discovered iridium
Iridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density of ...
in 1803.
* Jacques Amand Eudes-Deslongchamps (1794–1867), naturalist and palaeontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
.
* Eugène Eudes-Deslongchamps (1830–1889), paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
and naturalist
* Jules Lair
Jules–Auguste Lair (25 May 1836 – 16 May 1907) was a French lawyer, businessman and scholar.
At the École des Chartes he studied palaeography, and was offered a position with the Archives, but he decided instead to become a lawyer.
At the ag ...
(1836–1907), businessman, paleographer, historian and antiquary
* André-Louis Danjon
André-Louis Danjon (; 6 April 1890 – 21 April 1967) was a French astronomer born in Caen to Louis Dominique Danjon and Marie Justine Binet.
Danjon devised a method to measure "earthshine" on the Moon using a telescope in which a prism spl ...
(1890–1967), astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, natural satellite, moons, comets and galaxy, g ...
, measured the earthshine
Earthlight is the diffuse reflection of sunlight reflected from Earth's surface and clouds. Earthshine (an example of planetshine), also known as the Moon's ashen glow, is the dim illumination of the otherwise unilluminated portion of the Moon ...
on the moon
* René Herse (1908–1976), builder of high-quality touring, randonneur and racing bicycles.
* Jean-Yves Marin (born 1955), archeologist, medievalist and chief curator of French heritage.
* Pierre Denis (born 1964) businessman, CEO of Jimmy Choo Ltd
Jimmy Choo is a British high-end luxury fashion house specialising in shoes, handbags, accessories and fragrances. The company, J. Choo Limited, was founded in 1996 by Malaysian Chinese couture shoe designer Jimmy Choo and British ''Vogue'' ac ...
, 2012/2020.
Sport
 *
* René Menzies
René Menzies (c. November 1889 – c. 1971) was a French long-distance cyclist who at 48 held a record for the greatest distance ridden on a bicycle in a year. He rode in 1937. He was decorated with the Croix de Guerre in the First World War ...
(ca.1889 – ca.1971), long-distance cycling record holder
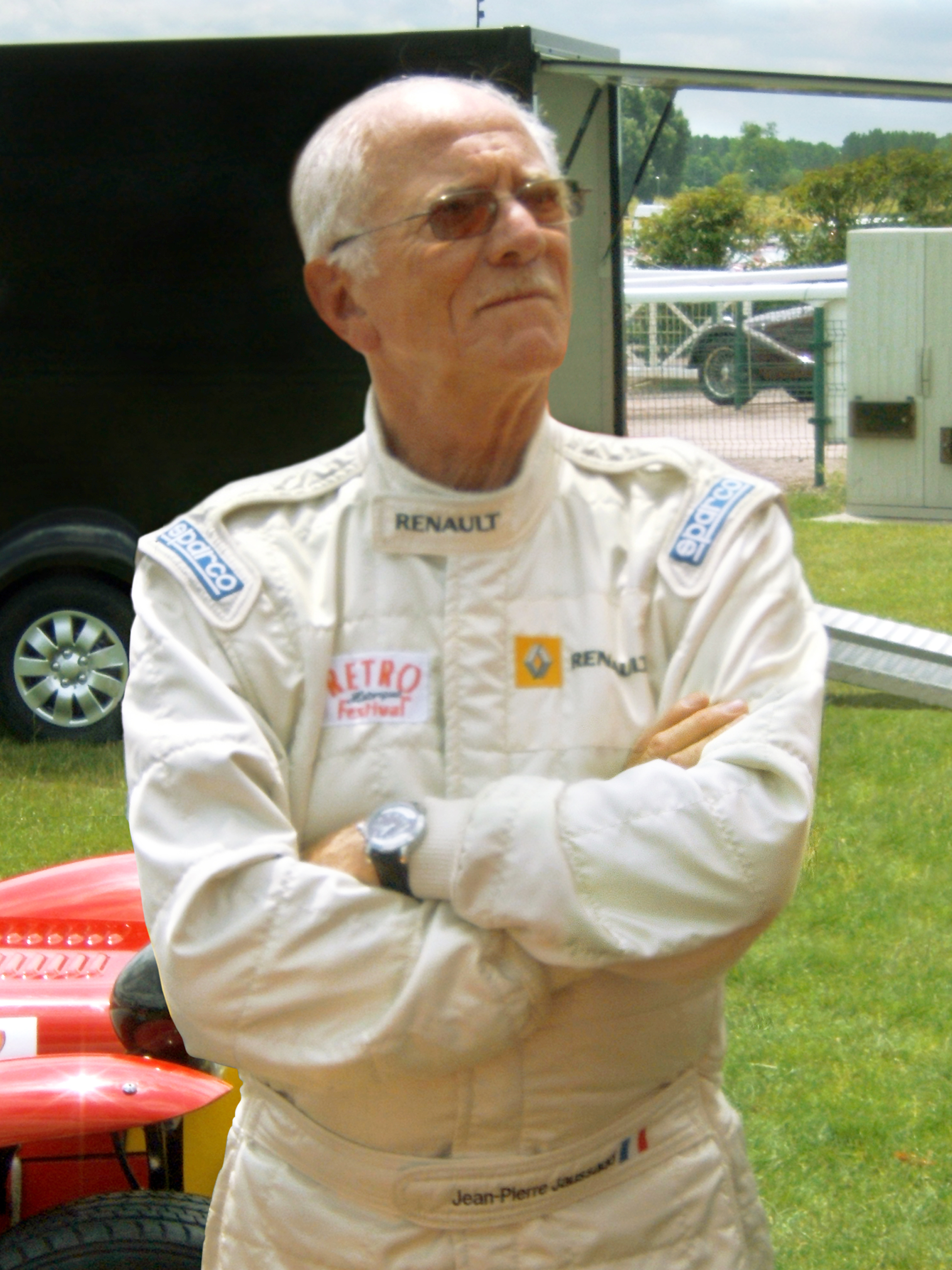
* Jean-Pierre Jaussaud
Jean-Pierre Jaussaud (3 June 1937 – 22 July 2021) was a French racing driver, noted for winning the 24 Hours of Le Mans in 1978 and 1980.
Jaussaud was born in Caen, Calvados, and started racing in automobiles in 1962, taking courses in the Jim ...
(1937–2021), racing driver, won the 24 Hours of Le Mans
The 24 Hours of Le Mans (french: link=no, 24 Heures du Mans) is an endurance-focused Sports car racing, sports car race held annually near the town of Le Mans, France. It is the world's oldest active Endurance racing (motorsport), endurance r ...
in 1978 and 1980.
* Jean-François Ballester (1965–2018), figure skater, gold medallist at the 2018 Winter Olympics
, nations = 93
, athletes = 2,922 (1,680 men and 1,242 women)
, events = 102 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening =
, closing =
, opened_by = President Moon Jae-in
, cauldron = Kim Yun-a
, stadium = Pyeongchang Olympic Stadium
, winte ...
* Corinne Lagache (born 1975), former football goalkeeper with 27 caps with France women
* Bruno Grougi (born 1983), a former footballer with 451 club caps and 3 for Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in th ...
* Jérémy Sorbon
Jérémy Sorbon (born 5 August 1983) is a French former professional footballer who played as a defender.
Career
Born in Caen, Sorbon spent large parts of his career at Stade Malherbe Caen, playing almost 300 games.
In June 2013, with his con ...
(born 1983), a former footballer with 518 club caps
* Benoît Costil
Benoît Guy Robert Costil (born 3 July 1987) is a French professional footballer who plays as a goalkeeper for club Lille.
Costil also is a French international, having represented his nation at under-21 and senior level. He represented his co ...
(born 1987), footballer with over 480 club caps and 1 for France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
* Youssef El-Arabi
Youssef El-Arabi (; born 3 February 1987) is a professional footballer who plays as a striker for Greek Super League club Olympiacos and the Morocco national team.
He began his career with hometown club Caen in Ligue 1, making his debut i ...
(born 1987), footballer with over 400 club caps and 46 for Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to ...
* Bruno Massot
Bruno Massot (born 28 January 1989) is a French-German pair skating coach and former competitor. Competing with Aljona Savchenko for Germany, he is the 2018 Olympic Champion, the 2018 World Champion, a two-time European silver medalist, and t ...
(born 1989), pair skater, gold medallist at the 2018 Winter Olympics
, nations = 93
, athletes = 2,922 (1,680 men and 1,242 women)
, events = 102 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening =
, closing =
, opened_by = President Moon Jae-in
, cauldron = Kim Yun-a
, stadium = Pyeongchang Olympic Stadium
, winte ...
International relations
Caen is twinned with: *Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria ...
, United States
* Nashville, Tennessee, Nashville, United States
* Ohrid, North Macedonia
* Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
, England, United Kingdom
* Reșița, Romania
* Thiès, Senegal
* Würzburg, Germany
* Anzio, Italy
Sport
Symbols
Heraldry
Current arms:''Gules, a single-towered open castle Or, windowed and masoned sable.''Under the Ancien Régime: ''Per fess, gules and azure, 3 fleurs de lys Or.'' During the First French Empire: ''Gules, a single-towered castle Or, a chief of Good Imperial Cities (gules, 3 bees Or).''
Motto
Today, Caen has no motto, but it used to have one, which did not survive the French Revolution. As a result, its spelling is archaic and has not been updated:''Un Dieu, un Roy, une Foy, une Loy.''(One God, one King, one Faith, one Law.) This motto is reflected in a notable old Chant royal.
Code
Caen's home port code is CN.Climate
Caen has an oceanic climate that is somewhat ameliorated due to its slightly inland position. In spite of this, summers are still cool by French standards and the climate is typically maritime in terms of high precipitation, relatively modest sunshine hours and mild winters.Gallery
See also
* * * Communes of the Calvados departmentReferences
Bibliography
* Joseph Decaëns and Adrien Dubois (ed.), ''Caen Castle. A ten Centuries Old Fortress within the Town'', Publications du CRAHM, 2010,Publications du CRAHM
External links
*Caen City Council
*
Encyclopædia Britannica Caen
Mémorial pour la Paix museum
Caen town guide
{{Authority control Caen, Communes of Calvados (department) Prefectures in France Port cities and towns on the French Atlantic coast Cities in France